
Response rates to anticonvulsant trials in patients with triphasic-wave EEG patterns of uncertain significance. How I treat patients with EEG patterns on the ictal-interictalcontinuum in the neuro ICU. Generalized periodic discharges with and without triphasic morphology.
Alkhachroum A.M., Al-Abri H., Sachdeva A. Comparison of triphasic waves and epilepticdischarges in one patient with genetic epilepsy. Generalized periodic discharges and “triphasic waves”: A blinded evaluation of inter-rater agreement and clinical significance. Triphasic waves versus nonconvulsivestatus epilepticus: EEG distinction. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus in the emergency room. Nonconvulsive status epilepticus EEG analysis in a large series. Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: a new look at GABA from the molecular standpoint. The pathophysiologic basis of hepatic encephalopathy: central role for ammonia andinflammation. Uncovering clinical and radiological associations of triphasic waves in acute encephalopathy: a case-control study. Triphasic waves and encephalopathy in the setting of pregabalin toxicity. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1988 70: 1–8. The diagnostic specificity of triphasic wave patterns. Niedermeyer's electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1984 57: 193–198. Triphasic waves: A reassessment of their significance. Hepatic coma: the electroencephalographic pattern. Significance of the electroencephalographic changes in hepatic coma. Standardized computer-based organized reporting of EEG: SCORE - Second version. Unified EEG terminology and criteria for nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Diagnostic accuracy between readers for identifying electrographic seizures in critically ill adults. An assessment of nonconvulsive seizures in the intensive care unit using continuous EEG monitoring: An investigation of variables associated with mortality. Acute seizures after intracerebral hemorrhage: A factor in progressive midline shift and outcome. Prevalence of nonconvulsive status epilepticus in comatose patients. 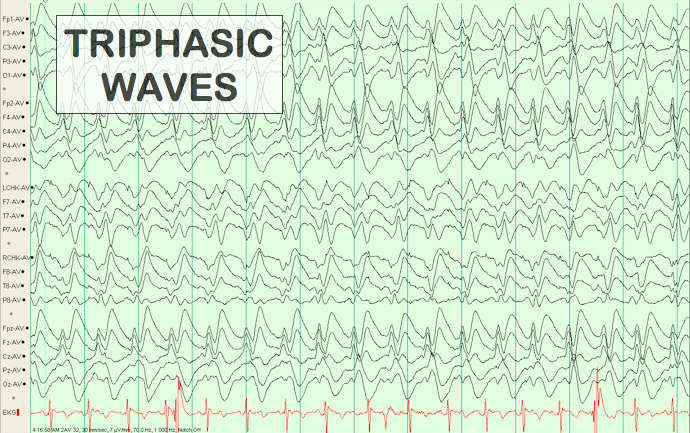 Towne A.R., Waterhouse E.J., Boggs J.G.
Towne A.R., Waterhouse E.J., Boggs J.G. 
Which EEG patterns in coma are nonconvulsive status epilepticus? Epilepsy Behav 2015 49: 203–222. Evidence-based guideline: treatment of convulsive status epilepticus in children and adults: report of the guideline committee of the American epilepsy society. Salzburg consensus criteria for non-convulsive status epilepticus - approach to clinical application.
Leitinger M., Beniczky S., Rohracher A. Affair with triphasic waves - their striking presence, mysterious significance, and cryptic origins: what are they? J Clin Neurophysiol 2015 32: 401–405. Classification and clinical significance. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Standardized Critical Care EEG Terminology: 2012 version. Atlas and classification of electroencephalography. Hepatic encephalopathy revisited: beyond the triphasic waves. Triphasic waves: swinging the pendulum back in this diagnostic dilemma. 
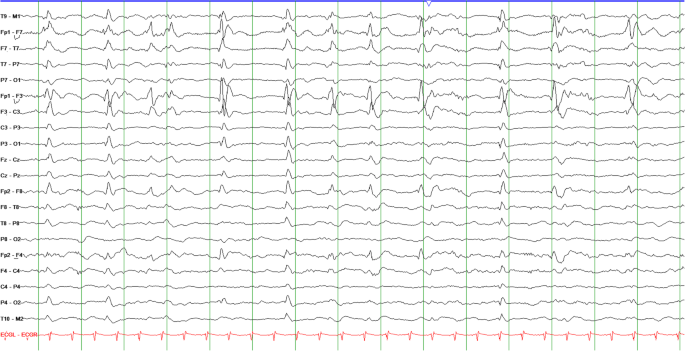
EEG monitoring must be performed in patients with a sudden deterioration of consciousness that cannot be explained by brain imaging studies. Utilization of the modern clinical and electrographic classifications enables the diagnosis of a nonconvulsive epileptic seizure and status epilepticus when the EEG pattern is ambiguous and traditionally associated with other conditions. Proper selection of the antiepileptic drugs along with monitoring of daily EEG recordings led to a recovery of consciousness in the patient and to normalization of the EEG pattern, which confirmed the clinical hypothesis of a nonconvulsive status epilepticus.Ĭonclusions. Description of the patient’s EEG according to the classification of rhythmic and periodic patterns of the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society and the use of clinical and EEG criteria of nonconvulsive status epilepticus of the International League Against Epilepsy enabled us to correctly diagnose the cause of her decreased alertness and other neurological symptoms. We present a case of diagnosis and successful treatment of a nonconvulsive status epilepticus, that developed in a female patient after CABG, and that presented electrographically as a triphasic wave pattern. The development of digital technologies and the introduction of systems that allow long-term EEG monitoring of the neurocritical care patients has led to accumulation of significant experience in recording triphasic waves in various metabolic, toxic, and structural brain disorders, as well as in nonconvulsive status epilepticus. Triphasic waves in an electroencephalogram (EEG) in patients with decreased alertness traditionally is associated with hepatic encephalopathy.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
